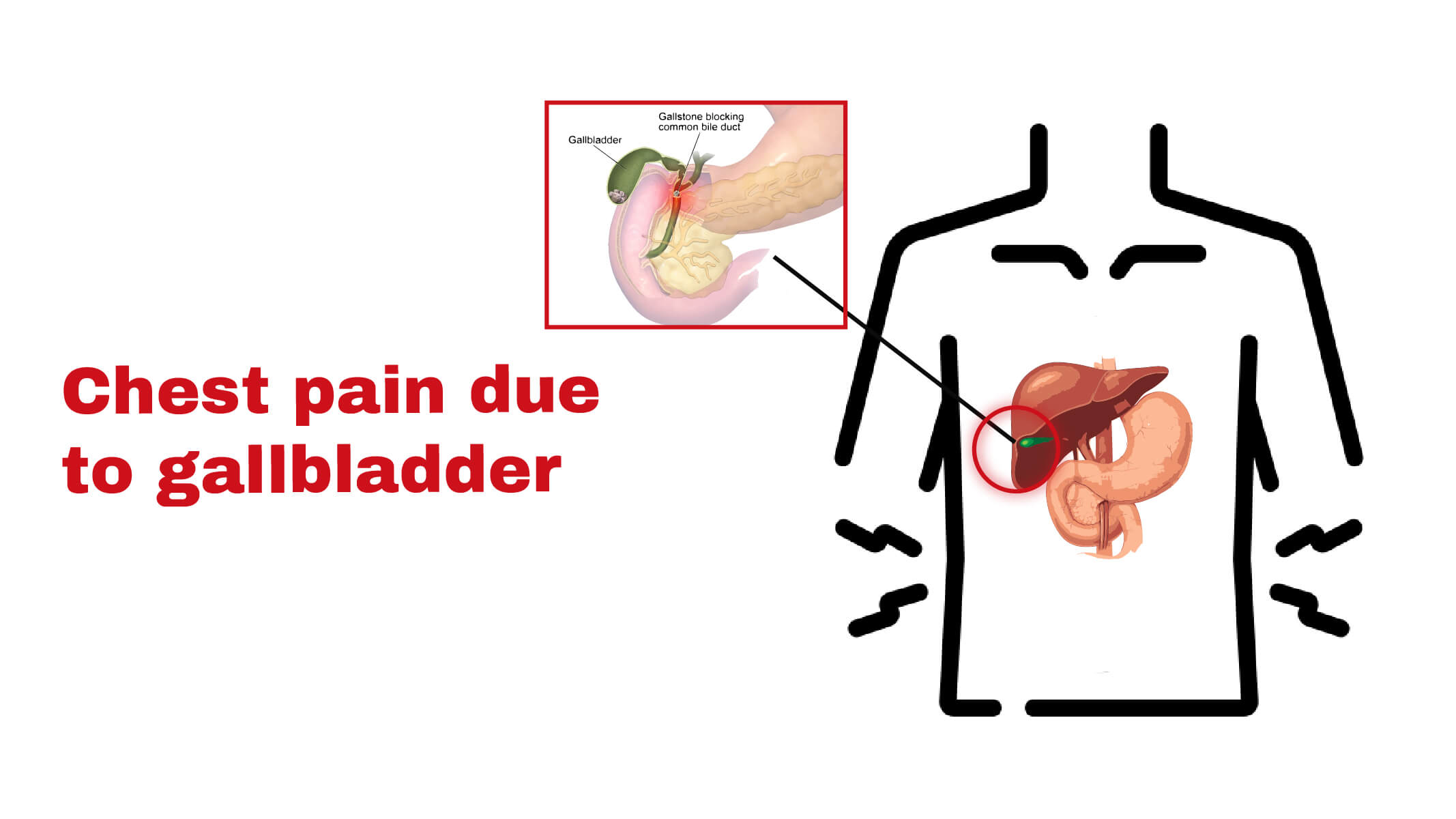
People ignore chest pain due to gallbladder. The problem in the gallbladder may be painful and need immediate medical recovery.
The gallbladder is a pear shape, 4-inch-long organ present under the liver in the upper right area of the abdomen. It stores the bile that digests fat and helps the body to absorb fat-soluble vitamins and nutrients. In a healthy gallbladder, functions and work happens painlessly. Where blockage occurs in the gallbladder causes poor function, pain, and discomfort. And this pain radiates toward the upper back and chest. The pain in the chest may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the condition. Chest pain due to gallbladder problem is like;
- Burning
- Crushing
- Squeezing
- Stabbing
- Ripping
- Aching
- Sharp
- Dull
- Intermittent
- Constant
Common problems of the gallbladder:
Some common problems of the gallbladder are;
- Gallstone (cholelithiasis)
The gallbladder stores or keeps bile which is a digestive fluid. Sometimes this digestive fluid becomes hardened, and stone is formed. And this condition can cause pain in the upper back region and chest. Harden piece or part of cholesterol or bile.
- Common bile duct stones (choledocholithiasis):
Bile is transported from the gallbladder through small bile ducts and deposited in the common bile ducts. From there, it moves toward the small intestine. Stones stay in the gallbladder for an extended period and then proceed to common bile ducts, called secondary common bile duct stones.
Suppose the stone in the common bile duct form it. It is called the primary common bile duct stone. These both cause pain that radiates toward the chest and upper back.
- Gallbladder cancer:
Gallbladder cancer is not very common, but it can spread to other body parts. Risk factors of gallbladder cancer are;
- Female
- Age
- Obesity
- Porcelain gallbladder
- Inflamed gallbladder (cholecystitis)
Sudden and acute gallbladder inflammation occurs when the bile cannot leave the gallbladder. Gallstone blocks the tube that transfers the bile in and out from the gallbladder.
- Perforated gallbladder:
When the gallstone leaves untreated, this can lead to a perforated gallbladder. In other words, a hole in the gallbladder wall occurs, and perforation becomes complicated.
- Bile duct infection:
Untreated bile duct can lead to infections. That may be a severe and life-threatening infection. It causes pain that tightens your chest.
- Chronic gallbladder disease:
Frequent episodes of gallstone attacks can cause permanent damage to the gallbladder. The gallbladder becomes ridge and scarred.
- Gallstone ileus:
Gallstone ileus is very rare but fatal. It happens when a gallstone goes toward the intestine and blocks it. Emergency medical attention and surgery are needed.
- Gallbladder abscess:
It is empyema when pus is developed in the gallbladder with a gallstone. It produces severe pain in the abdomen and chest.
- Gallbladder polyps:
The growth of polyps in the gallbladder causes no harm, but large polyps need treatment. Symptoms can cause severe problems.
Can gallbladder cause chest pain on the left side?
Many people suffer from chest pain due to gallbladder disease. Gallstone and other gallbladder diseases can cause extreme muscle spasms and pressure in the upper right stomach that moves toward the chest. This pain feels on the left side of the chest. Gallbladder attacks cause pain that moves to the upper back and behind the breastbone (left side of the chest). It is the same as a heart attack.
Symptoms of gallbladder chest pain:
Signs and symptoms of chest pain due to gallbladder problems are;
- Pain in the middle of the abdomen
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Chills
- Severe chest pain
- Changes in urine
- Changes in bowel movements
- Jaundice
When to see the doctor:
Seek immediate medical attention if the symptoms get worsen, such as;
- Upper-right pain in the chest
- High fever and chills
- Nausea or vomiting
- Severe abdominal pain
- Frequent bowel movements and urination
Diagnosis:
The following are the methods or techniques that are used to diagnose gallbladder problems;
- Gallbladder imaging test:
CT scan and Ultrasound are used to create a clear image of the gallbladder.
- Test to examine bile duct:
MRI, hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid scans, and an endoscopy retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) are the tests used to check or examine the bile duct.
- Blood tests:
Doctors do many blood tests to check the gallbladder’s cause of pancreatitis, infection, and inflammation.
Risk factors of gallbladder disease:
Risk factors for gallbladder diseases are;
- Unhealthy lifestyle
- Overweight
- Age
- Genetics
- High cholesterol
- Diet with high fat and low fiber
- Chronic diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease, sickle cell anemia, and diabetes
- Excess use of medications
- Women Pregnancy
Gallbladder diet:
Diet for a healthy gallbladder is s low-fat diet and best to lose weight. A balanced diet and variety of foods will never cure the gallbladder. Diet for these patients includes;
- Eat high-fiber foods:
Beans, peas, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Reduce carbohydrates and sugar intake.
- Consume fats that are healthy or good for you, like olive oil and fish oil.
Treatment of chest pain gallbladder:
There is not as much to treat the gallstones. One can try applying the warm compress to that affected area. Traditional treatment is to do surgery to remove the gallstone. One can prevent gallstones by reducing the intake of fatty foods and managing weight. The following terms can reduce the chances of gallbladder and chest pain;
- Exercise:
Regular exercise and physical activity can reduce the chances of gallstones and prevent chest pain.
- Eat more fiber:
Eat more fiber from veggies, whole grain foods, and fruits that contain a lot of fiber.
- Lose weight:
Try to lose weight slowly because quick weight loss can increase the chances of gallstones and increase heartbeats.
- Eat properly:
Don’t skip meals and don’t do fasting; this may increase the chances of gallstone formation, which leads to chest pain.
- Medicines:
Only take prescribed medicines. Other medicines increase the risk, such as postmenopausal hormones.
- Eat more magnesium:
Some studies show that eating more magnesium can reduce the risk of gallstone formation, which can lead to chest pain.
References:
https://www.ncbi.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5696806/
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/311357
https://www.urgencyroom.com/blogpost?id=1015
https://www.dailyitem.com/chest-pain-may-be-gallbladder-disease/article_b4950c07-eb34-5415-a50a-06321972f97e.html
https://www.medicinenet.com/chest_pain_on_the_left_side_above_a_female_breast/article.htm
https://dighealth.org/posts/recognizing-a-gallbladder-attack/